Blog / Guide
Write to UsDatacenter vs Residential Proxies
October 15, 2025
Guide

Datacenter vs Residential Proxies
Datacenter proxies are fast and cost-effective server-based IPs; residential proxies are real-home IPs prized for authenticity. Below, we break down how each works, where they shine, and how IP rotation impacts reliability and detection.
What Are Datacenter Proxies?
Datacenter proxies are the "factory-made" version of IP addresses. They come from servers sitting in commercial data centers rather than from homes or real users. Because of that, they can be created in large numbers very quickly. Datacenter proxies work by routing your traffic through proxy servers located in data centers, often provided by cloud service providers, which supply the IP addresses used in these proxies. The proxy server acts as an intermediary, masking your real IP address and separating you from the internet. These proxies are part of a larger proxy network managed by providers, and are commonly used to access websites anonymously.
The big advantage here is speed and cost. Since they run on powerful server hardware, they're fast and usually very stable. Datacenter proxies provide stable and predictable proxy connections, making them suitable for high-volume tasks. They operate independently of your original internet connection, offering flexibility and anonymity regardless of your local network setup. Need a batch of a thousand IPs for a big scraping job? A provider can set that up almost instantly. Datacenter proxies can support multiple users simultaneously, which can affect reliability and increase the risk of detection or IP blocking. Within datacenter proxies, you can choose between shared proxies and dedicated proxies, with dedicated proxies offering higher privacy and reliability for specialized applications. For things like automated testing or large SEO projects, that speed is hard to beat.
The flip side is detection. Websites know which IP ranges belong to data centers. Datacenter proxies hide your real IP address and location, but they are easier to detect and block compared to residential proxies. If you hammer a site with too many requests, it won't take long for your traffic to get flagged. Choosing between datacenter proxies and other types, such as ISP or residential proxies, depends on your specific needs—balancing legitimacy, performance, accuracy, and speed for tasks like web scraping or bypassing anti-bot protections.
What Are Residential Proxies?
Residential proxies are a different story. These proxies are IP addresses assigned to actual devices in real households, originating from home internet networks. The IPs come from real Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and are tied to actual devices, such as computers and mobile phones, connected to home internet networks. When you connect through one, your request is routed through a genuine home connection, and the proxy uses a real IP address provided by an internet service provider (ISP). This means residential proxies leverage real residential IPs, making them appear more genuine and increasing their legitimacy. Residential proxies work by masking your actual IP address and true IP address, mimicking real user behavior to provide privacy and security. Residential IP addresses come from diverse locations worldwide, thanks to residential networks that provide geographic diversity for proxy IPs. To the target website, it looks like a normal person sitting at their laptop, making your traffic look like it comes from a real user.
That authenticity is their superpower. Because they look like ordinary traffic and are linked to actual devices, residential proxies are far harder to detect and block. That's why marketers, e-commerce teams, and even individual users often rely on them when accuracy and trust matter more than raw speed. Residential proxies are assigned through an internet service provider (ISP), and unlike residential proxies, ISP proxies are provided directly by ISPs and are not sourced from user devices, which affects their authenticity and use cases.
Of course, this comes with a price. Residential proxies are harder to source and maintain, so they usually cost more. They can also be a bit slower depending on the household connection you're routed through, and the number of devices connected to the home network can affect proxy performance. Residential proxies may also face ISP constraints that can impact speed and reliability.
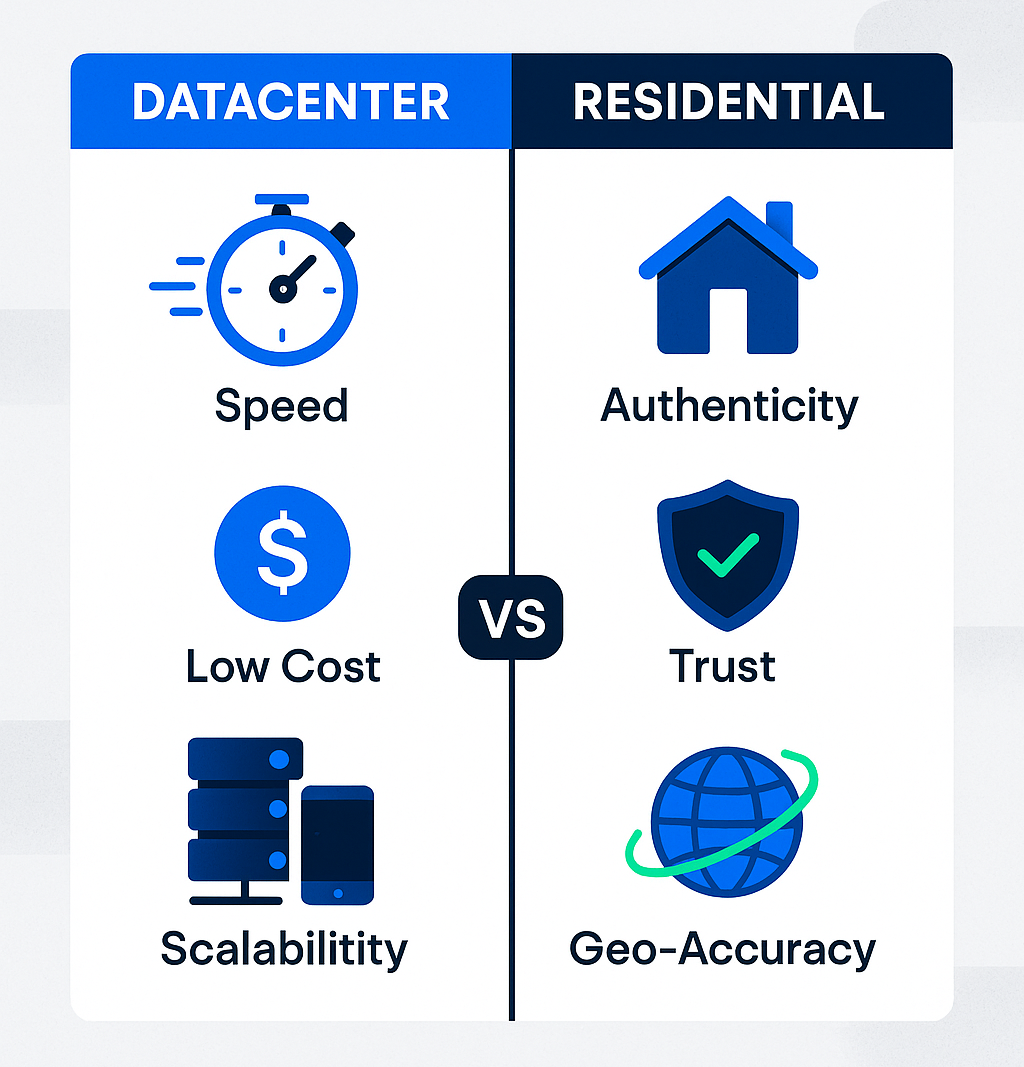
Datacenter vs Residential Proxies: Key Differences
The key differences between datacenter and residential proxies are crucial for users to understand when choosing the right solution. Datacenter proxies are built for scale, offering cheap, fast, and easily created IPs in bulk, making them ideal for tasks requiring speed and efficiency. In contrast, residential proxies are built for stealth, originating from real devices, providing high anonymity, and being much harder to block.
When comparing residential and dedicated proxies, it's important to note that residential proxies offer greater legitimacy and lower detectability, while dedicated proxies provide exclusive use and consistent performance. Residential and datacenter proxies also differ in their sources and use cases: residential proxies come from real users' devices and are best for web scraping, geo-locating, and avoiding detection, while datacenter proxies come from data centers and are preferred for tasks that require speed and cost-effectiveness.
Proxy locations play a significant role in effective proxy usage, as choosing the right geographic diversity can help bypass geo-restrictions and improve anonymity for activities like market research and web scraping. Managing multiple accounts is a common use case for proxies, especially for tasks such as performance testing and AI training. Social media management often relies on the right proxy type to maintain anonymity and avoid bans when handling several accounts.
Finally, selecting a reliable proxy service is essential to ensure clean, trustworthy IP addresses, maintain anonymity, and avoid blacklisting for uninterrupted online activities.
That's why you'll often hear people say: use datacenter proxies when you can, and residential proxies when you have to.
IP Address and Rotation: How They Work and Why They Matter
Every time you connect to the internet, your device is assigned an IP address—a unique string of numbers that acts like your digital home address. In the world of datacenter and residential proxies, how these IP addresses are sourced and rotated makes all the difference in how well your proxy setup works.
With residential proxies, the IP addresses come straight from internet service providers (ISPs) and are assigned to real devices in actual homes. This means when you use a residential proxy, your web requests look like they're coming from a genuine user on a home network. That's why residential proxies are so effective for accessing geo-restricted content, managing multiple social media accounts, or slipping past anti-bot systems—because to the target website, you appear as just another regular visitor.
Datacenter proxies, on the other hand, use IP addresses generated in bulk by powerful servers in data centers. These data center IPs aren't tied to any specific ISP or physical location, which makes them fast and easy to scale. However, because many websites can spot the difference between a data center IP and a real residential IP, datacenter proxies are more likely to get flagged if you're making lots of requests or trying to access restricted websites.
That's where IP rotation comes in. Proxy providers use IP rotation to automatically switch the IP address your connection uses at regular intervals or with each new request. This makes it much harder for websites to detect patterns and block your activity. For example, if you're scraping data from a site or running SEO monitoring across thousands of pages, rotating through a pool of different IP addresses helps you avoid getting blacklisted.
Residential proxies tend to use real IP addresses assigned by ISPs, so rotating through them keeps your activity looking authentic. Datacenter proxy providers offer private datacenter proxies and dedicated datacenter proxies that rotate data center IPs to reduce the risk of detection. Shared datacenter proxies are more budget-friendly but may be slower if multiple users are accessing the same proxy server at once.
The choice between datacenter and residential proxies—and how you use IP rotation—depends on your goals. If you need speed and volume for tasks like market research, ad verification, or bulk web scraping, datacenter proxies with smart IP rotation can get the job done efficiently. But if you're trying to access geo-restricted content, manage multiple social media platforms, or avoid anti-bot systems, residential proxies with real IP addresses assigned by ISPs are your best bet for staying under the radar.
Mobile proxies are another option, using IP addresses assigned by mobile carriers. These are especially useful for tasks that require the highest level of trust and stealth, like accessing mobile-specific data or bypassing tough web security measures. Like other proxy types, mobile proxies also rely on IP rotation to keep your activity anonymous and unblockable.
In short, understanding how IP addresses and IP rotation work is key to choosing the right proxy type for your needs. Whether you're after the speed and scale of datacenter proxies or the authenticity and stealth of residential proxies, using a proxy provider that offers robust IP rotation will help you maintain reliable connections, avoid IP blocking, and achieve your online goals—no matter how challenging the target.

When Datacenter Proxies Make Sense
Imagine an SEO agency that has to track rankings for 20,000 keywords every day across multiple markets. They need speed and lots of IPs to handle the volume. Datacenter proxies are perfect for this because they're affordable and can deliver results quickly.
They're also useful for stress-testing websites, running bulk automations, or scraping sites that don't have very aggressive protections. In short, if the risk of being blocked is low and cost is a concern, datacenter proxies are usually the go-to option.
When Residential Proxies Are the Better Choice
Now picture an online retailer trying to monitor competitor prices across Europe. If they rely on datacenter proxies, the target sites may catch on and block their requests. With residential proxies, the requests look like they're coming from ordinary shoppers in Paris, Berlin, or Milan. The data is accurate, and the chances of being flagged are much lower.
Or think about an ad campaign. You launch ads in five different countries, and you want to see how they actually appear to local users. A datacenter proxy might show a blank page or get stopped. A residential proxy shows you the ad exactly as a customer would see it.
Even sneaker resellers and gaming enthusiasts use them because websites running limited releases often block datacenter IP ranges. Residential proxies are especially effective for accessing websites that block datacenter IPs, allowing users to bypass restrictions and access content as if they were genuine customers. A residential proxy slips through because it looks like a genuine customer's connection.
Why Many Businesses Use Both
It doesn't always have to be a choice of datacenter vs residential proxies. In fact, the smartest companies combine them.
Datacenter proxies handle the heavy lifting — bulk scraping, SEO monitoring, and high-volume tasks. Residential proxies are saved for the sensitive stuff — ad verification, geo-specific research, and any situation where being blocked would ruin the project.
This mixed approach balances costs with effectiveness. You don't overspend on residential IPs for tasks that don't need them, but you also don't risk losing access when accuracy matters most.

Legal and Ethical Side
Both types of proxies are legal to use. They're simply tools for routing traffic differently. What matters is your intent. Checking prices, researching competitors, or running marketing campaigns are all legitimate. Illegal uses remain illegal, proxy or no proxy.
With residential proxies, ethics come into play as well. A trustworthy provider will only include devices in their network when the owners know about it and give consent, often with compensation. It's always worth asking your provider how they source their IPs.
Conclusion
When it comes to datacenter vs residential proxies, the right choice depends on your goals. If you need speed, volume, and affordability, datacenter proxies are the clear winner. If you require authenticity, stealth, and reliable access to geo-specific data, residential proxies are the smarter option.
In practice, many businesses combine both: datacenter proxies handle large-scale tasks, while residential proxies provide the accuracy and trust needed for sensitive or location-specific projects.
At LightningProxies, we provide access to both datacenter and residential proxy solutions in one place, giving you the flexibility to scale efficiently while maintaining precision and reliability. By understanding the strengths of each type, you can confidently choose the right tool for your needs and avoid the setbacks that come from relying on the wrong option.

September 29, 2025
Guide
What Is a Residential Proxy: Complete Guide 2025
Learn everything about residential proxies: how they work, types, benefits, and use cases for web scraping and privacy.

October 22, 2025
Comparison
Proxy vs VPN: What's the Difference & Which One Should You Use?
Learn the key differences between proxies and VPNs, including speed, security, and use cases. Discover why proxies are often better for business operations.

October 03, 2025
Announcements
Proxy Meaning: What Does a Proxy Really Do
Discover the true meaning of proxy servers and how they work.





